The Biodiversity Information Standards (TDWG) annual conference was, like so many others, an online-only experience. With an audience of uber-nerds who inhabit the fine niche of taxonomy, systematics and biodiversity informatics – this posed no issue!
There was a fine range of symposia and discussion sessions to choose from. These annual conferences serve two purposes:
- to provide a forum for developing, refining, and extending standards in response to new challenges and opportunities; and
- to provide a showcase for biodiversity informatics – much of which relies on the standards created by TDWG and other organizations.
Data standards that describe and support the exchange of biodiversity information are critical scientific infrastructure. They enable data to be integrated in support of research, decision-making and conservation planning. Ultimately, standards extend the usability of data across taxa, scientific disciplines, and administrative boundaries.
Gaia Resources now has a long history of actively participating in TDWG. Having attended my first conference in Reading, UK in 1998, I became the Oceania representative from 2002-2008, and in the year I took my leave from that position Gaia Resources played a major role in helping host the conference in Fremantle, WA.
This year a small team here prepared an interesting case study for presentation in the conference session entitled “Avenues into integration: communicating taxonomic intelligence from sender to recipient”, organised by researchers from Arizona State University. Serge, Kehan, Jason and I worked on exploring ways of validating taxonomic names data embedded within environmental impact assessments and survey reports. This was spurred by two initiatives:
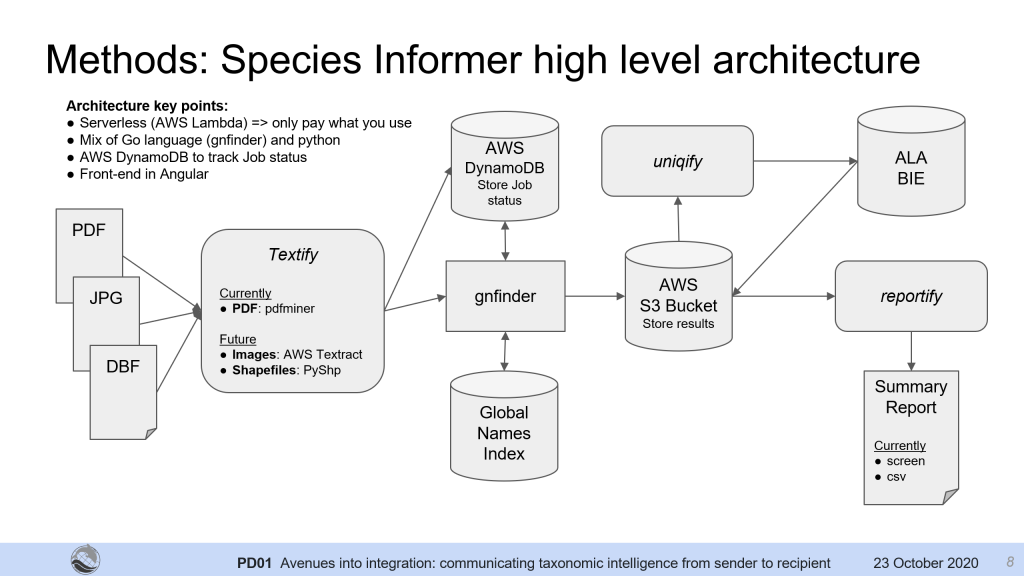
- the availability of a new and improved taxonomic names interrogator – GNfinder, that significantly improves the speed of finding and retrieving taxonomic name strings from a document with references to the Global Names Index, and
- the availability of IBSA – an open repository of environmental surveys in Western Australia.
The result was a small prototype we called ‘Species Informer’.
We created a procedure for uploading PDF documents, analysing taxonomic names, and then interrogating the Atlas of Living Australia for ancillary data for those names, such as local conservation status, in order to provide an automated summary of taxon names issues within each document for further analysis. We also ran a small test on image-only data using AWS Textract, to extract text from documents scanned as images to use as well.
Preliminary findings, from a small sample, included:
- gnfinder speeds the process of finding taxon names uttered in a document
- of course, it finds all taxon name mentions, not just the relevant ones for the survey
- we didn’t explore the gnfinder options for sensitivity, data source or context searching
- Species Informer produces a CSV report in c. 1 minute, as opposed to perhaps 8 hours for manual verification
- at a c. 90% success rate for finding taxon names in a report, environment officers still need to check the whole document
- not currently included in the Global Names Index are ‘phrase name taxa’ – c. 7% (1,143 of the 15,558) of the native vascular plant taxa in WA, and c. 15% (558 of the 3,782) of conservation taxa.
Some primary conclusions from this study included that ‘data governance’ is required at all parts of the process:
- preparing the source report to ensure all taxa are resolved
- the taxon names available to the Global Names Index could be expanded to include authenticated unpublished (phrase) names
- the regular maintenance of name currency, conservation status and child taxon information is necessary
conservation status needs to be better maintained at regional, national, global levels.
The video of is now available so you can hear the presentation and see the detailed results of our study. In fact, I would commend all presentations for viewing as many innovative methods for communicating taxonomic intelligence from sender to recipient were presented.
If you’d like to know more about this project, please drop me a line at alex.chapman@gaiaresources.com.au, or connect with us on Twitter, LinkedIn or Facebook.
Alex

Comments are closed.